Refrigerant, also known as refrigerant, is the working substance in the refrigeration system. At present, there are more than 80 kinds of substances that can be used as refrigerants. The most common refrigerants are Freon (including: R22, R134a, R407c, R410a, R32, etc.), ammonia (NH3), water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2) , a small number of hydrocarbons (such as: R290, R600a).
The impact indicators of refrigerants on the global environment mainly include: ozone depletion potential (ODP) and global warming potential (GWP); in addition to the impact on the environment, refrigerants should also have acceptable safety to protect people’s lives and property .
ODP Ozone Depletion Potential: Indicates the ability of chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere to destroy the ozone layer. The smaller the value, the better the environmental characteristics of the refrigerant. Refrigerants with ODP values less than or equal to 0.05 are considered acceptable based on current levels.
GWP Global Warming Potential: An indicator of the climate impact caused by greenhouse gas emissions, indicating that within a certain period of time (20 years, 100 years, 500 years), the greenhouse effect of a certain greenhouse gas corresponds to the quality of CO2 with the same effect, CO2 The GWP=1.0. Usually calculate GWP based on 100 years, denoted as GWP100, “Montreal Protocol” and “Kyoto Protocol” both use GWP100.
1. Classification of refrigerants
According to GB/T 7778-2017, refrigerant safety is subdivided into 8 categories, namely: A1, A2L, A2, A3, B1, B2L, B2, B3, among which A1 is the safest and B3 is the most dangerous.
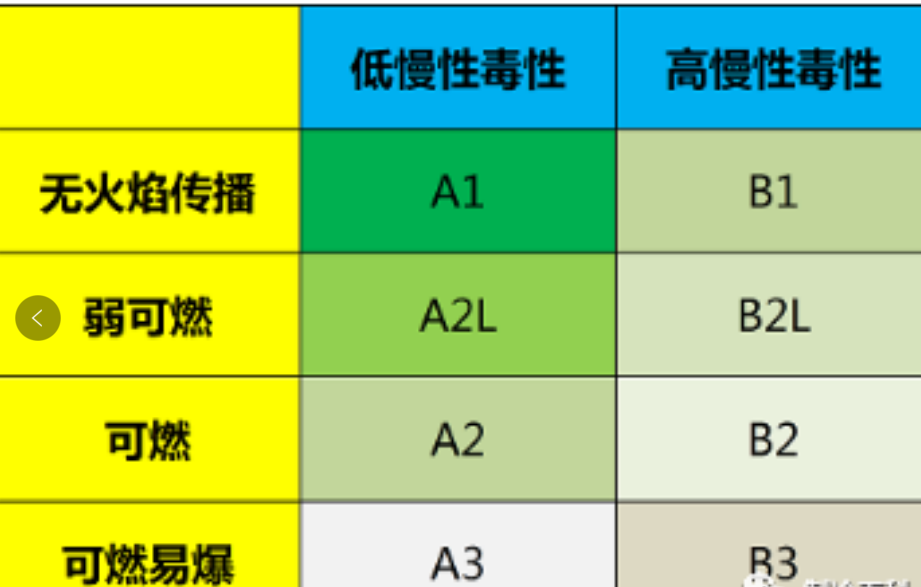
The safety levels of common refrigerants are as follows:
Type A1: R11, R12, R13, R113, R114, R115, R116, R22, R124, R23, R125, R134a,, R236fa, R218, RC318, R401a, R401b, R402a, R402b, R403a, R403b, R404a, R407a, R407b, R407c, R407d, R408a, R409a, R410a, R417a, R422d, R500, R501, R502, R507a, R508a, R508b, R509a, R513a, R744
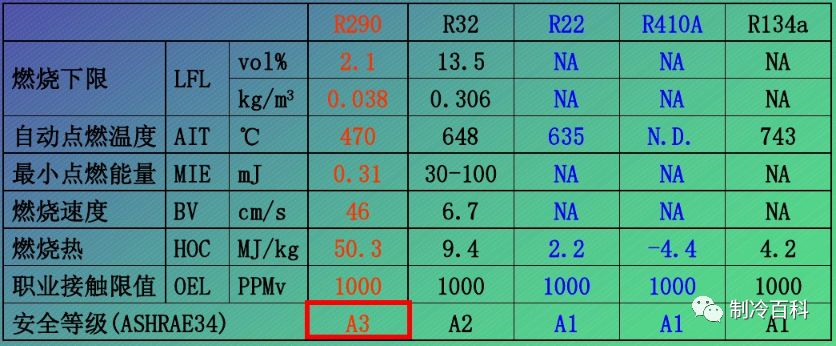
Type A2: R142b, R152a, R406a, R411a, R411b, R412a, R413a, R415b, R418a, R419a, R512a
A2L category: R143a, R32, R1234yf, R1234ze(E)
Class A3: R290, R600, R600a, R601a, R1270, RE170, R510a, R511a
Category B1: R123, R245fa
B2L category: R717
According to the evaporation temperature ts of the refrigerant under standard atmospheric pressure (100kPa), it can be divided into: high-temperature refrigerant, medium-temperature refrigerant, and low-temperature refrigerant.
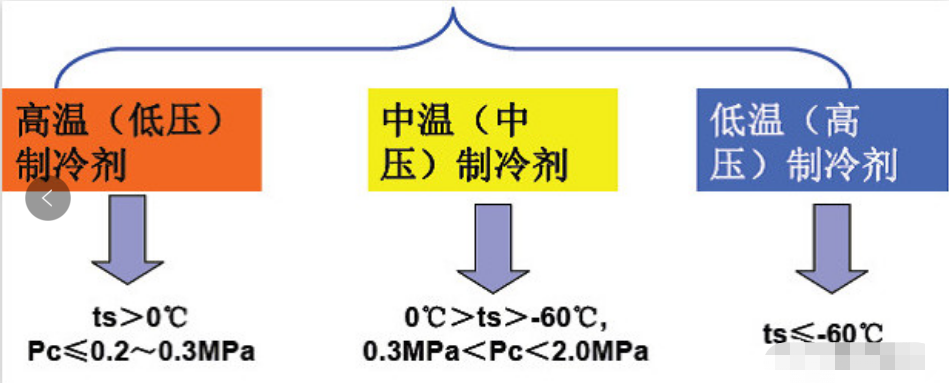
Low-pressure high-temperature refrigerant: the evaporation temperature is higher than 0°C, and the condensation pressure is lower than 29.41995×104Pa. These refrigerants are suitable for use in centrifugal refrigeration compressors in air conditioning systems.
Medium-pressure medium-temperature refrigerant: medium-pressure medium-temperature refrigerant: evaporation temperature -50 ~ 0°C, condensing pressure (196.113 ~ 29.41995) × 104Pa. This type of refrigerant is generally used in ordinary single-stage compression and two-stage compression piston refrigeration systems.
High-pressure and low-temperature refrigerant: high-pressure and low-temperature refrigerant: the evaporation temperature is lower than -50°C, and the condensation pressure is higher than 196.133×104Pa. This type of refrigerant is suitable for the low-temperature part of the cascade refrigeration device or the low-temperature device below -70°C.
Post time: Dec-28-2022







