Thermal expansion valve, capillary tube, electronic expansion valve, three important throttling devices
The throttling mechanism is one of the important components in the refrigeration device. Its function is to reduce the saturated liquid (or subcooled liquid) under the condensing pressure in the condenser or liquid receiver to the evaporation pressure and evaporation temperature after throttling. According to the change of load, the flow of refrigerant entering the evaporator is adjusted. Commonly used throttling devices include capillary tubes, thermal expansion valves, and float valves.
If the amount of liquid supplied by the throttling mechanism to the evaporator is too large compared to the load of the evaporator, part of the refrigerant liquid will enter the compressor together with the gaseous refrigerant, causing wet compression or liquid hammer accidents.
On the contrary, if the amount of liquid supply is too small compared with the heat load of the evaporator, part of the heat exchange area of the evaporator will not be able to fully function, and even the evaporation pressure will be reduced; and the cooling capacity of the system will be reduced, the cooling coefficient will be reduced, and the compressor The discharge temperature rises, which affects the normal lubrication of the compressor.
When the refrigerant fluid passes through a small hole, a part of the static pressure is converted into dynamic pressure, and the flow rate increases sharply, becoming a turbulent flow, the fluid is disturbed, the frictional resistance increases, and the static pressure decreases, so that the fluid can achieve the purpose of reducing the pressure and regulating the flow.
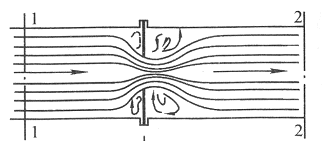
Throttling is one of the four main processes indispensable to the compression refrigeration cycle.
The throttling mechanism has two functions:
One is to throttle and depressurize the high-pressure liquid refrigerant coming out of the condenser to the evaporation pressure
The second is to adjust the amount of refrigerant liquid entering the evaporator according to system load changes.
1. Thermal expansion valve
Thermal expansion valve is widely used in Freon refrigeration system. Through the function of temperature sensing mechanism, it automatically changes with the temperature change of the refrigerant at the outlet of the evaporator to achieve the purpose of adjusting the liquid supply amount of the refrigerant.

Most thermal expansion valves have their superheat set at 5 to 6°C before leaving the factory. The structure of the valve ensures that when the superheat is increased by another 2°C, the valve is in the fully open position. When the superheat is about 2°C, the expansion valve will is closed. The adjustment spring for controlling the superheat, the adjustment range is 3~6℃.
Generally speaking, the higher the degree of superheat set by the thermal expansion valve, the lower the heat absorption capacity of the evaporator, because increasing the degree of superheat will take up a considerable part of the heat transfer surface at the tail of the evaporator, so that the saturated steam can be superheated here. It occupies a part of the heat transfer area of the evaporator, so that the area of the refrigerant vaporization and heat absorption is relatively reduced, that is to say, the surface of the evaporator is not fully utilized.
However, if the degree of superheat is too low, the refrigerant liquid may be brought into the compressor, resulting in the unfavorable phenomenon of liquid hammer. Therefore, the regulation of superheat should be appropriate to ensure that sufficient refrigerant enters the evaporator while preventing liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor.
The thermal expansion valve is mainly composed of a valve body, a temperature sensing package and a capillary tube. There are two types of thermal expansion valve: internal balance type and external balance type according to different diaphragm balance methods.
Internally balanced thermal expansion valve
Internally balanced thermal expansion valve is composed of valve body, push rod, valve seat, valve needle, spring, regulating rod, temperature sensing bulb, connecting tube, sensing diaphragm and other components.
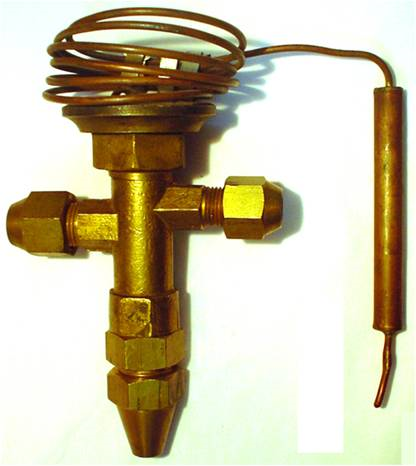



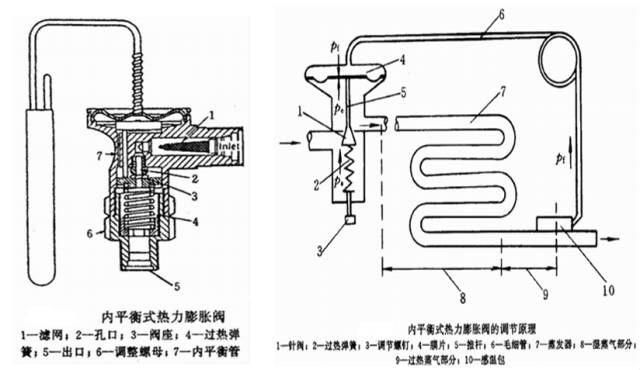
Externally balanced thermal expansion valve
The difference between the external balance type thermal expansion valve and the internal balance type in structure and installation is that the space under the external balance valve diaphragm is not connected with the valve outlet, but a small diameter balance pipe is used to connect with the evaporator outlet. In this way, the refrigerant pressure acting on the underside of the diaphragm is not Po at the inlet of the evaporator after throttling, but the pressure Pc at the outlet of the evaporator. When the force of the diaphragm is balanced, it is Pg=Pc+Pw. The opening degree of the valve is not affected by the flow resistance in the evaporator coil, thus overcoming the shortcomings of the internal balance type. The external balance type is mostly used in the occasions where the evaporator coil resistance is large.
Usually, the steam superheat degree when the expansion valve is closed is called the closed superheat degree, and the closed superheat degree is also equal to the open superheat degree when the valve hole starts to open. The closing superheat is related to the preload of the spring, which can be adjusted by the adjustment lever.
The superheat when the spring is adjusted to the loosest position is called the minimum closed superheat; on the contrary, the superheat when the spring is adjusted to the tightest is called the maximum closed superheat. Generally, the minimum closed superheat degree of the expansion valve is not more than 2℃, and the maximum closed superheat degree is not less than 8℃.
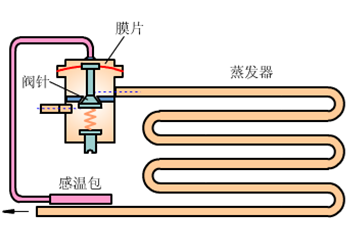
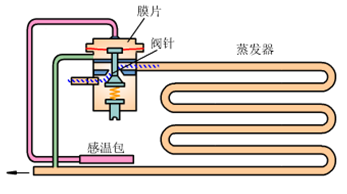
For the internal balance thermal expansion valve, the evaporation pressure acts under the diaphragm. If the resistance of the evaporator is relatively large, there will be a large flow resistance loss when the refrigerant flows in some evaporators, which will seriously affect the thermal expansion valve. The working performance of the evaporator increases, resulting in an increase in the superheat degree at the outlet of the evaporator, and an unreasonable utilization of the heat transfer area of the evaporator.
For externally balanced thermal expansion valves, the pressure acting under the diaphragm is the outlet pressure of the evaporator, not the evaporation pressure, and the situation is improved.
2. Capillary
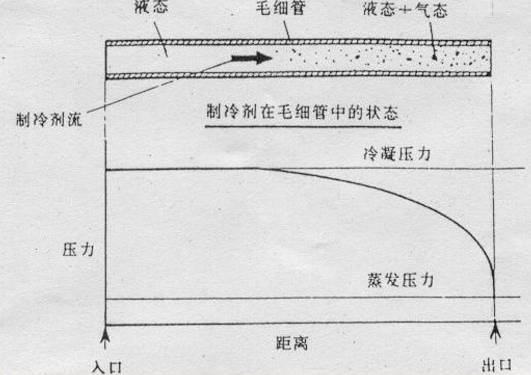
The capillary is the simplest throttling device. The capillary is a very thin copper tube with a specified length, and its inner diameter is generally 0.5 to 2 mm.
Features of capillary as throttling device
(1) The capillary is drawn from a red copper tube, which is convenient to manufacture and cheap;
(2) There are no moving parts, and it is not easy to cause failure and leakage;
(3) It has the characteristics of self-compensation,
(4) After the refrigeration compressor stops running, the pressure on the high-pressure side and the pressure on the low-pressure side in the refrigeration system can be quickly balanced. When it starts running again, the motor of the refrigeration compressor starts.

3. Electronic expansion valve
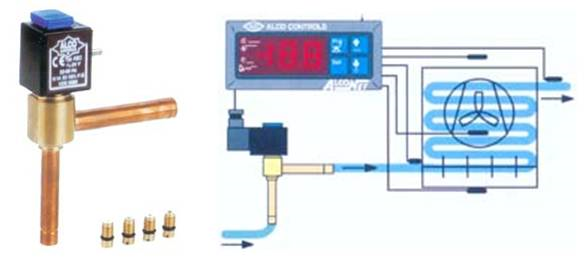
The electronic expansion valve is a speed type, which is used in the intelligently controlled inverter air conditioner. The advantages of the electronic expansion valve are: a large flow adjustment range; high control accuracy; suitable for intelligent control; suitable for rapid changes in high-efficiency refrigerant flow.
Advantages of Electronic Expansion Valves
Large flow adjustment range;
High control precision;
Suitable for intelligent control;
Can be applied to rapid changes in refrigerant flow with high efficiency.
The opening of the electronic expansion valve can be adapted to the speed of the compressor, so that the amount of refrigerant delivered by the compressor matches the amount of liquid supplied by the valve, so that the capacity of the evaporator can be maximized and the optimal control of the air conditioning and refrigeration system can be achieved.
The use of electronic expansion valve can improve the energy efficiency of the inverter compressor, realize rapid temperature adjustment, and improve the seasonal energy efficiency ratio of the system. For high-power inverter air conditioners, electronic expansion valves must be used as throttling components.
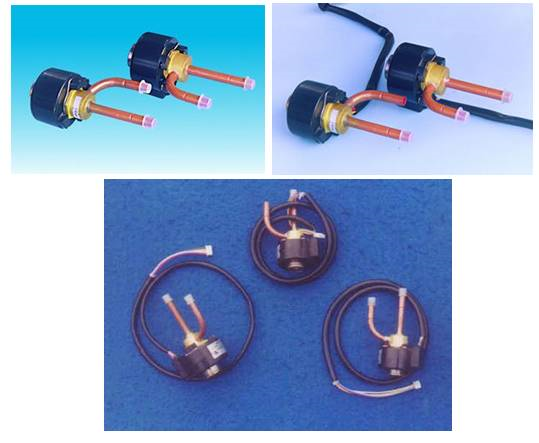

The structure of the electronic expansion valve consists of three parts: detection, control and execution. According to the driving method, it can be divided into electromagnetic type and electric type. Electric type is further divided into direct-acting type and deceleration type. The stepping motor with a valve needle is a direct-acting type, and the stepping motor with a valve needle through a gear set reducer is a deceleration type.
Post time: Nov-25-2022







